When it comes to treating periodontitis, finding an effective medication is crucial for successful outcomes. Periodontitis is a serious gum infection that damages the soft tissue and destroys the bone supporting the teeth. Without proper treatment, it can lead to tooth loss and other health complications.
Recent studies have shown the efficacy of certain medications in the treatment of periodontitis. These medications not only help to reduce inflammation and control bacterial growth, but they also promote tissue regeneration and repair. Finding the right medication in consultation with a dental professional is key to effectively managing periodontitis and maintaining oral health.
Effective Medication for Periodontitis Treatment: A Comprehensive Overview
When it comes to treating periodontitis effectively, the role of medications is crucial in managing the condition. Understanding the various medications available and how they work can significantly impact the treatment outcomes for patients with periodontitis. In this comprehensive overview, we will explore the different types of medications used in periodontitis treatment, their mechanisms of action, and considerations for choosing the right medication.
1. Antibiotics for Periodontitis
One common medication type used in periodontitis treatment is antibiotics. These medications are often prescribed to eliminate or control the bacteria causing the infection in the gums. Antibiotics may be taken orally or applied directly to the infected areas. Websites like WebMD provide detailed information on the types of antibiotics used for periodontitis and their potential side effects. It is essential to follow your dentist’s recommendations when using antibiotics for periodontitis treatment.
2. Antimicrobial Mouthwashes
Antimicrobial mouthwashes are another type of medication that can be beneficial in managing periodontitis. These mouthwashes contain active ingredients that help reduce the bacteria in the mouth, promoting healing and preventing further infection. Websites like Colgate offer insights into the best antimicrobial mouthwashes for periodontitis treatment. Incorporating antimicrobial mouthwash into your daily oral hygiene routine can complement professional treatment and aid in controlling the progression of periodontitis.
3. Pain Management Medications
Periodontitis can cause discomfort and pain for patients, especially during advanced stages of the condition. Pain management medications, such as over-the-counter pain relievers or prescription medications, may be recommended to alleviate symptoms. Websites like Healthline provide guidance on the use of pain management medications for periodontitis and their potential interactions with other drugs. It is important to discuss any pain or discomfort with your dentist to determine the most suitable medication for your needs.
Understanding the Role of Medications in Periodontitis Management
Effective management of periodontitis often involves a combination of professional dental treatments and medications to control the infection and promote gum health. Understanding how medications play a role in periodontitis management can empower patients to take an active part in their oral health care. In this section, we will delve into the significance of medications in managing periodontitis and their impact on treatment outcomes.
1. Controlling Bacterial Infections
Medications play a crucial role in controlling bacterial infections in the gums, which are the primary cause of periodontitis. By targeting specific bacteria with antibiotics or antimicrobial agents, medications can help reduce inflammation and prevent the progression of the disease. Websites like the American Dental Association (ADA) provide resources on the importance of controlling bacterial infections in periodontitis management through appropriate medication use.
2. Supporting Healing and Tissue Regeneration
Some medications used in periodontitis treatment are designed to support healing and tissue regeneration in the gums. These medications may stimulate the growth of healthy gum tissue and promote the repair of damaged areas. Websites like Perio.org offer insights into the role of medications in supporting tissue regeneration and the benefits of incorporating these medications into comprehensive periodontal therapy.
3. Managing Symptoms and Discomfort
In addition to treating the underlying infection, medications can also help manage symptoms and discomfort associated with periodontitis. Pain relievers, anti-inflammatory drugs, and other medications can offer relief from gum pain, swelling, and sensitivity. Websites like the Mayo Clinic provide information on symptom management in periodontitis and the role of medications in improving patient comfort during treatment.
Key Considerations for Choosing the Right Medication
When selecting medications for periodontitis treatment, several considerations must be taken into account to ensure the effectiveness and safety of the chosen treatment plan. Understanding these key considerations can help patients and dental professionals make informed decisions regarding medication choices. In this section, we will outline important factors to consider when choosing the right medication for managing periodontitis.
1. Individual Patient Needs
Each patient’s condition and medical history are unique, requiring personalized treatment approaches. When choosing medications for periodontitis, considering the patient’s overall health, allergies, and potential drug interactions is essential. Websites like PubMed Health provide resources on personalized medicine and the importance of tailoring treatment plans to individual patient needs.
2. Treatment Goals and Outcomes
Defining clear treatment goals and desired outcomes is crucial in selecting the right medications for periodontitis management. Whether the focus is on controlling infection, reducing inflammation, or promoting tissue regeneration, aligning medication choices with treatment objectives can enhance the chances of successful outcomes. Websites like the National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research (NIDCR) offer guidance on setting treatment goals in periodontitis and selecting medications accordingly.
3. Adherence to Treatment Plans
Adherence to prescribed medication regimens is vital for the effectiveness of periodontitis treatment. Patients must follow their dentist’s instructions regarding medication dosage, frequency, and duration to achieve optimal results. Websites like Drugs.com provide tools and resources to help patients track their medication adherence and stay informed about the importance of following treatment plans accurately.
**
Types of Medication for Advanced Periodontitis Management
**
Periodontitis is a severe form of gum disease that requires specialized medication to manage effectively. There are several types of medication commonly used in the treatment of advanced periodontitis, each serving a specific purpose in combating the disease.
1. **Antibiotics**: Antibiotics are often prescribed to patients with advanced periodontitis to help eliminate the bacteria causing the infection. These medications can be taken orally or applied directly to the infected gums to target the harmful bacteria and reduce inflammation.
2. **Antimicrobial Mouthwash**: In addition to antibiotics, antimicrobial mouthwashes are frequently recommended as part of the treatment plan for advanced periodontitis. These mouthwashes contain active ingredients that help kill bacteria in the mouth and prevent further infection.
3. **Anti-inflammatory Drugs**: To reduce inflammation and manage pain associated with advanced periodontitis, anti-inflammatory drugs may be prescribed. These medications can help alleviate discomfort and promote healing in the gums.
4. **Bone-Enhancing Medications**: In cases where advanced periodontitis has led to bone loss in the jaw, bone-enhancing medications may be used to help regenerate bone tissue and support the teeth.
5. **Pain Relievers**: Pain relievers such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen may be recommended to patients with advanced periodontitis to manage discomfort during treatment.
**
Insights into Periodontitis Medication and Gum Disease Prevention
**
Periodontitis medication plays a crucial role not only in treating the disease but also in preventing the progression of gum disease. By understanding the importance of medication and implementing preventive measures, individuals can maintain optimal oral health and reduce the risk of advanced periodontitis.
1. **Regular Dental Check-ups**: Routine visits to the dentist for cleanings and check-ups are essential for monitoring gum health and detecting any signs of periodontitis early on. Dentists can recommend appropriate medication and treatments to prevent the disease from advancing.
2. **Proper Oral Hygiene**: Brushing twice a day, flossing regularly, and using antimicrobial mouthwash can help remove plaque and bacteria from the teeth and gums, reducing the risk of gum disease.
3. **Healthy Lifestyle Choices**: Eating a balanced diet, avoiding tobacco products, and managing stress can contribute to overall oral health and prevent gum disease.
4. **Educational Resources**: Understanding the causes and symptoms of periodontitis can empower individuals to take proactive measures in preventing the disease. Educational resources provided by healthcare professionals can offer valuable insights into gum disease prevention.
5. **Collaborative Care**: Working closely with a dental team and following their recommendations for medication and treatment can enhance the effectiveness of periodontitis management and promote gum disease prevention.
**
Innovative Approaches to Medication in Periodontitis Treatment
**
Advancements in dental care have led to innovative approaches to medication in the treatment of periodontitis. These new methods and technologies aim to enhance the effectiveness of treatment, improve patient outcomes, and provide alternative options for managing gum disease.
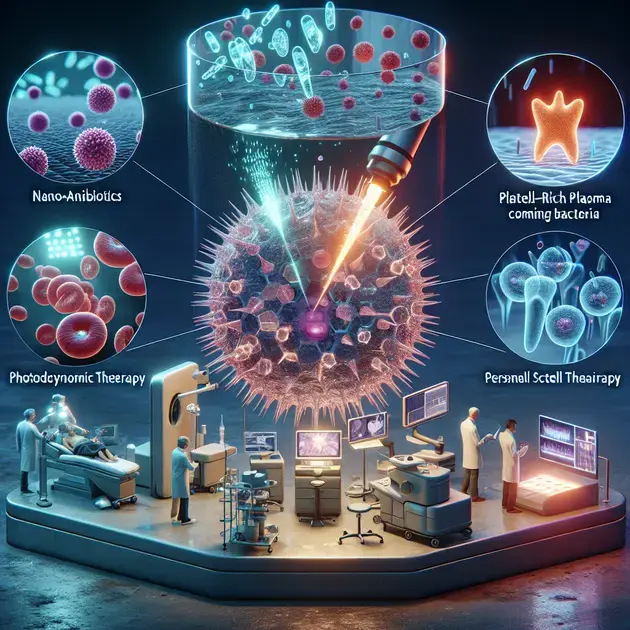
1. **Nano-antibiotics**: Nano-antibiotics are a novel approach to delivering antibiotics directly to the site of infection in a more targeted and effective manner. These tiny particles can penetrate biofilms and reach deep into periodontal pockets to combat bacteria more efficiently.
2. **Platelet-rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy**: PRP therapy involves using a patient’s own blood plasma, rich in growth factors, to promote tissue regeneration and accelerate healing in the gums. This innovative approach can enhance the effects of traditional periodontitis medication.
3. **Photodynamic Therapy**: Photodynamic therapy utilizes a combination of light and photosensitizing agents to target and destroy bacteria in the gums. This non-invasive treatment can supplement traditional medication and improve the overall success of periodontitis management.
4. **Stem Cell Therapy**: Stem cell therapy holds promise in regenerating damaged gum tissue and bone lost to periodontitis. By harnessing the regenerative capabilities of stem cells, this innovative approach can aid in restoring oral health and function.
5. **Personalized Medication**: With advancements in genetic testing and personalized medicine, healthcare providers can tailor medication regimens to individual patients’ unique needs and genetic predispositions. This personalized approach can optimize the effectiveness of periodontitis treatment and improve patient outcomes.
Conclusion
Effective management of advanced periodontitis necessitates a combination of specialized medications tailored to combat the disease’s progression. Antibiotics play a crucial role in eliminating harmful bacteria, while antimicrobial mouthwashes aid in preventing further infection. Anti-inflammatory drugs not only reduce inflammation but also promote healing in the gums, crucial for overall recovery.
Furthermore, bone-enhancing medications offer support and regeneration in cases of bone loss, ensuring the preservation of teeth and oral structure. Pain relievers provide necessary relief during treatment, enhancing patient comfort and compliance. These medications collectively form a comprehensive approach to tackling advanced periodontitis effectively.
Gum disease prevention and periodontitis medication go hand in hand in maintaining optimal oral health. Regular dental check-ups, proper oral hygiene practices, and healthy lifestyle choices play pivotal roles in preventing the disease’s progression. Empowering individuals with educational resources and promoting collaborative care with dental professionals are essential strategies in comprehensive gum disease prevention.
Recent advancements in periodontitis treatment have brought forth innovative approaches to medication. Nano-antibiotics offer targeted delivery for enhanced efficacy, while Platelet-rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy accelerates tissue regeneration. Photodynamic Therapy and Stem Cell Therapy provide non-invasive yet effective solutions for combating bacteria and regenerating damaged tissues.
Personalized medication, driven by genetic testing and tailored to individual needs, represents a significant leap in optimizing treatment outcomes. These innovative approaches supplement traditional medication, promising improved patient outcomes and a more precise, patient-centric treatment experience. By embracing these advancements in periodontitis medication, patients can look forward to enhanced care and better oral health in the future.



